The Quick Sort algorithm is one of the most commonly used sorting algorithms.
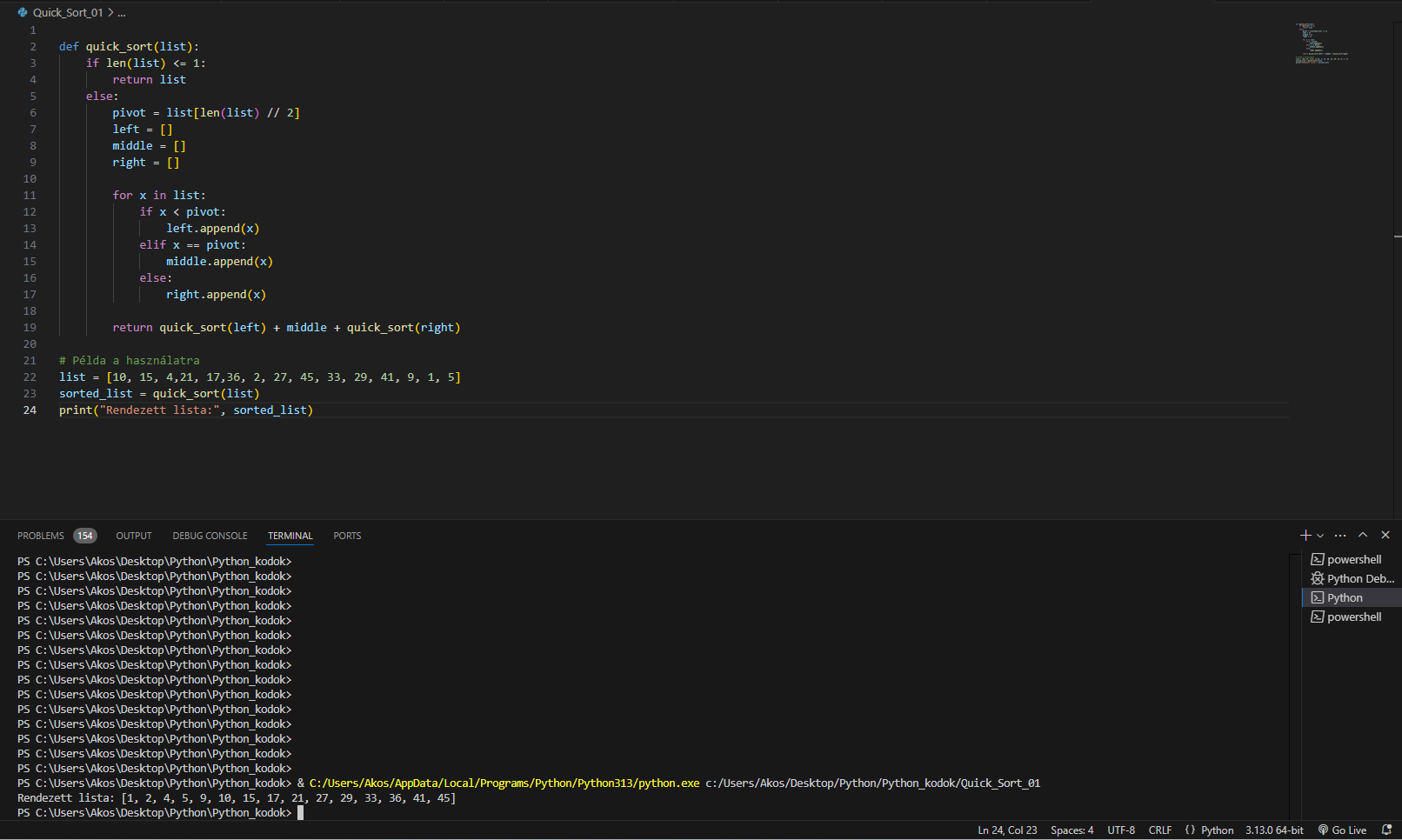
After running the code in Visual Studio, as shown in the command prompt at the bottom of the screen (recommended to view in full-screen mode), you can see that the list defined in the code is sorted in ascending order.
How Quick Sort Works (Collapsible content – click the + icon on the far right)
The Quick Sort algorithm is a divide-and-conquer sorting algorithm. Its operation involves the following steps:
1. Selecting a Pivot The first step in Quick Sort is choosing a pivot element. The pivot can be any element in the list, such as the first, last, or middle element. This pivot serves as the basis for sorting the other elements.
Partitioning
A következő lépésben az algoritmus a pivot elem köré rendezi az elemeket:
All elements smaller than the pivot are placed before it. All elements larger than the pivot are placed after it. Once this is done, the pivot is swapped into its correct position in the list.
3. Recursive Sorting
After placing the pivot in its correct position, the algorithm recursively calls itself on the sublists to the left and right of the pivot (the pivot itself is not included, as it is already sorted).
The process is repeated for both smaller and larger elements on the left and right sides. The recursion continues until each sublist contains only one or no elements, at which point they are considered sorted.
4. Completion
The recursion ends for all levels once all sublists are sorted. The algorithm finally returns a fully sorted list by combining the sorted sublists.
Code Snippet: (Expandable content – click the + icon on the right.)
def quick_sort(list):
if len(list) <= 1:
return list
else:
pivot = list[len(list) // 2]
left = []
middle = []
right = []
for x in list:
if x < pivot:
left.append(x)
elif x == pivot:
middle.append(x)
else:
right.append(x)
return quick_sort(left) + middle + quick_sort(right)
# Példa a használatra
list = [10, 15, 4,21, 17,36, 2, 27, 45, 33, 29, 41, 9, 1, 5]
sorted_list = quick_sort(list)
print("Rendezett lista:", sorted_list)

